
IOP Reduction Calculator
Intraocular Pressure Calculator
Estimate how brinzolamide eye drops may reduce your intraocular pressure (IOP) based on current measurements.
When doctors talk about controlling brinzolamide in glaucoma, they’re really discussing a drug that quietly lowers the pressure inside your eye, protecting the optic nerve from damage. This article breaks down exactly what brinzolamide does, why it matters for people with glaucoma, and how it fits into everyday treatment plans.
Key Takeaways
- Brinzolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (CAI) that reduces intraocular pressure (IOP) by decreasing aqueous humor production.
- It’s delivered as a preservative‑free eye‑drop formulation, making it a good option for patients sensitive to preservatives.
- When combined with prostaglandin analogs or beta‑blockers, brinzolamide can achieve target IOP in most patients.
- Common side effects include a bitter taste and temporary blurred vision, but serious adverse events are rare.
- Regular monitoring and adherence are essential to maintain long‑term visual health.
What is Brinzolamide?
Brinzolamide is a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (CAI) used to lower intra‑ocular pressure in patients with open‑angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2003, it is marketed under the brand name Azopt and comes in a preservative‑free 1% ophthalmic solution.
Why Intra‑ocular Pressure Matters
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is the fluid pressure inside the eye. In a healthy eye, a balance exists between aqueous humor production and drainage. When that balance tips, pressure rises and can damage the optic nerve, leading to progressive vision loss-what doctors call glaucoma.
How Brinzolamide Lowers IOP
The drug works by inhibiting the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, which is crucial for bicarbonate production in the ciliary body. Less bicarbonate means reduced aqueous humor secretion, and consequently lower IOP.
In pharmacodynamic terms, a single drop reduces IOP by about 20‑25% within 1-2hours, with the effect lasting up to 12hours. Because the formulation is preservative‑free, it’s gentler on the ocular surface, a key consideration for patients on multiple drops.
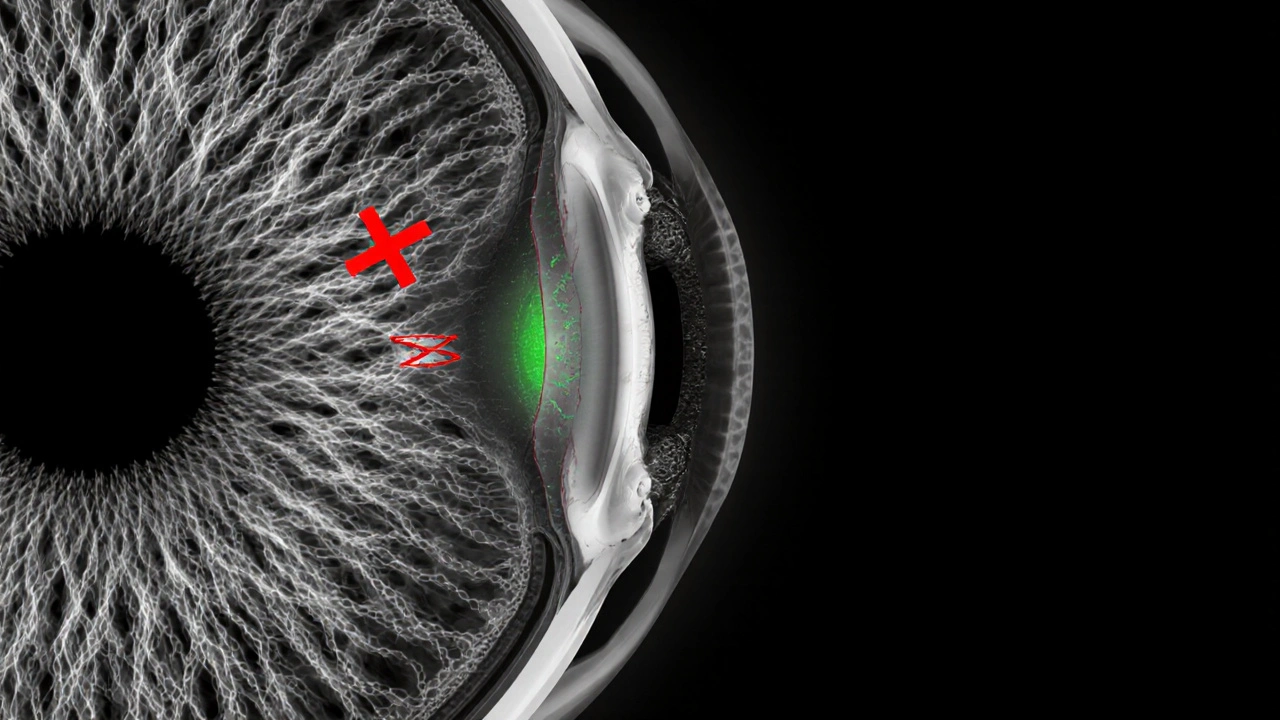
Where Brinzolamide Fits in Treatment Algorithms
Current glaucoma guidelines (e.g., American Academy of Ophthalmology 2024) place brinzolamide in the “second‑line” tier, often after a prostaglandin analog (like latanoprost) fails to hit target IOP. It can also serve as a “partner drug” in fixed‑combination regimens.
Typical step‑wise approach:
- Start with a prostaglandin analog once daily. \n
- If IOP remains >21mmHg, add brinzolamide BID (twice daily).
- For insufficient control, consider a beta‑blocker (e.g., timolol) or a rho‑kinase inhibitor.
Comparing Brinzolamide with Other Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
| Attribute | Brinzolamide | Dorzolamide | Timolol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor | Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor | Beta‑blocker |
| Concentration | 1% (preservative‑free) | 2% (contains benzalkonium chloride) | 0.5% (contains benzalkonium chloride) |
| Dosing frequency | BID | BID | Once daily |
| IOP reduction (average) | 22‑25% | 20‑23% | 25‑30% |
| Common side effects | Bitter taste, transient blurred vision | Burning, stinging | Bradycardia, fatigue |
| Contraindications | Severe sulfa allergy | Severe sulfa allergy | Asthma, severe COPD, bradycardia |
Practical Tips for Using Brinzolamide Eye Drops
- Timing: Install drops twice a day, ideally 12hours apart (e.g., morning and night).
- Technique: Pull down the lower eyelid, squeeze one drop, close eyes gently for 1‑2minutes, then blot excess with a tissue. Avoid blinking hard.
- Interaction with other drops: Wait at least 5minutes before applying a second medication to prevent wash‑out.
- Storage: Keep the bottle at room temperature, away from direct sunlight. Discard after 30days of opening.
- Adherence monitoring: Use a medication diary or smartphone reminder; missed doses can quickly raise IOP.
Side Effects and Safety Profile
Most patients tolerate brinzolamide well. The most reported local reactions are:
- Bitter or metallic taste (occurs in ~5% of users).
- Transient blurred vision or mild eye irritation.
Systemic absorption is minimal, so serious systemic effects are rare. However, because brinzolamide contains a sulfonamide moiety, anyone with a severe sulfa allergy should avoid it.
If you notice persistent eye redness, pain, or significant vision changes, contact your eye‑care professional promptly-these could signal an allergic reaction or secondary glaucoma.
Monitoring and Follow‑up
After initiating therapy, schedule an IOP check within 4-6weeks. Goal IOP depends on disease severity, but most clinicians aim for at least a 20% reduction from baseline or an absolute pressure <18mmHg.
Long‑term monitoring includes:
- Tonometry (IOP measurement) at every visit.
- Optic nerve imaging (OCT) every 6‑12months.
- Visual field testing annually.
Adherence data from pharmacy refill records can also flag patients who may need counseling.
When to Switch or Add Other Medications
If brinzolamide alone doesn’t achieve target pressure, consider these options:
- Combine with a prostaglandin analog (e.g., latanoprost) for additive effect.
- Add a beta‑blocker (timolol) if systemic contraindications are absent.
- Use a fixed‑combination drop (e.g., brinzolamide/timolol) to simplify dosing.
Patients with severe disease may eventually need laser therapy (SLT) or surgical intervention (trabeculectomy).
Frequently Asked Questions
How quickly does brinzolamide start working?
Most patients notice a drop in IOP within 1-2hours after the first dose, with the peak effect around 4hours.
Can I use brinzolamide with my prostaglandin eye drops?
Yes. Brinzolamide is often added to a prostaglandin regimen when a single medication doesn’t reach the target IOP. Apply the prostaglandin drop first, wait 5minutes, then use brinzolamide.
What should I do if I miss a dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for the next scheduled dose. In that case, skip the missed one and continue with your regular schedule-don’t double‑dose.
Is brinzolamide safe for people with asthma?
Unlike beta‑blockers, brinzolamide does not affect the lungs, so it’s generally safe for asthmatics, provided they have no sulfa allergy.
Can I drive after using brinzolamide?
Most people experience only mild, temporary blurred vision. If you feel any visual disturbance, wait until it clears before driving.





Comments (16)
Amit Kumar
Great rundown on brinzolamide! 🌟 The preservative‑free drops are a blessing for patients with sensitive eyes, and the 20‑25% IOP drop is solid. 👍 Keep the tips coming!
Crystal Heim
The mechanism is simple carbonic anhydrase inhibition reduces aqueous humor production and thus intraocular pressure
Abhimanyu Singh Rathore
Indeed, the inhibition of carbonic anhydrase-an enzyme crucial for bicarbonate formation in the ciliary body-directly curtails aqueous humor secretion! This biochemical cascade, when interrupted, yields a measurable decline in intra‑ocular pressure, typically observed within one to two hours post‑administration. Moreover, the preservative‑free formulation mitigates ocular surface irritation, a factor often overlooked in clinical discussions! 🌟
Stephen Lewis
While the preceding explanation is thorough, it is pertinent to underscore the importance of adherence to dosing intervals, particularly the recommended twelve‑hour spacing, to sustain therapeutic efficacy and minimize rebound IOP elevation. Additionally, periodic monitoring remains indispensable to tailor treatment to individual patient response.
janvi patel
Not everyone needs a second‑line CAI; some patients do just fine on monotherapy.
Lynn Kline
Absolutely, while monotherapy can be sufficient in select cases, the diversity of glaucoma phenotypes often warrants a multimodal approach; integrating brinzolamide can enhance IOP control, especially when prostaglandin analogues plateau. Moreover, the preservative‑free nature adds a layer of ocular comfort, a subtle yet significant benefit for long‑term adherence.
Rin Jan
Brinzolamide works by targeting the enzyme carbonic anhydrase in the ciliary body. By inhibiting this enzyme the production of bicarbonate is reduced. This leads to less aqueous humor being secreted into the anterior chamber. With less fluid the intra‑ocular pressure drops steadily over the next few hours. Patients typically notice a reduction of about twenty to twenty‑five percent within two hours. The effect can last up to twelve hours which makes twice‑daily dosing practical. Because the formulation is preservative‑free it is gentler on the ocular surface. This is especially important for individuals who require multiple eye drops. Combining brinzolamide with a prostaglandin analogue often achieves target pressure when monotherapy fails. The safety profile is favourable with most side effects limited to a bitter taste or mild transient blur. Systemic absorption is minimal so systemic adverse events are rare. However patients with severe sulfa allergy should avoid this medication. Regular follow‑up appointments allow clinicians to adjust therapy based on measured IOP. Using a diary or smartphone reminder can improve adherence and prevent pressure spikes. Overall brinzolamide offers a valuable option in the glaucoma treatment algorithm for many patients.
Jessica Taranto
Thank you for the comprehensive walk‑through; the step‑by‑step timeline you provided really clarifies what patients can expect during the first half‑day after instillation. It also highlights the importance of scheduling follow‑ups around that window.
akash chaudhary
Your appreciation, while courteous, glosses over a critical point: the pharmacokinetic profile of brinzolamide mandates strict adherence; any deviation can precipitate sub‑therapeutic IOP control, thereby accelerating optic nerve damage. The data unequivocally demonstrate a dose‑response relationship, and laxity is unacceptable.
kenneth strachan
OMG, I thought all CAIs were the same, but brinzolamide actually feels like the underdog hero in the eye drop saga-surprisingly effective and way less irritating than dorzolamide.
Mandy Mehalko
Yea, totally! It’s cool how brinzolamide sneaks in without the sting and still does the job. Keep spreading the word!
Bryan Kopp
While the drug works, let’s remember that innovation in eye care should stay home‑grown.
Patrick Vande Ven
The efficacy of brinzolamide is supported by multinational clinical trials, irrespective of the origin of the pharmaceutical development. Regulatory approvals across jurisdictions attest to its universal applicability.
Tim Giles
Indeed, the cross‑regional studies provide a robust evidence base; however, it would be remiss not to examine the pharmacoeconomic implications of incorporating brinzolamide into standard treatment protocols, particularly in health systems with constrained resources. Moreover, long‑term adherence patterns merit further investigation to ascertain whether the preservative‑free formulation translates into measurable improvements in patient‑reported outcomes over extended follow‑up periods.
Peter Jones
All perspectives considered, brinzolamide appears to fill a niche for patients needing additional pressure control without adding preservative burden, and clinicians should weigh its benefits against individual tolerance and cost.
Scott Davis
Well said.